Vocal Cord Nodules: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Causes
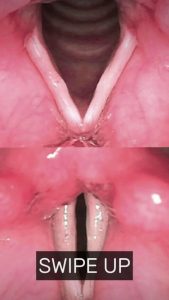
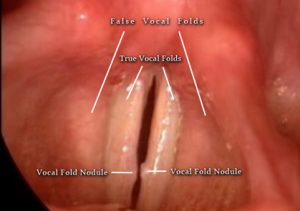
Vocal cord nodules, also known as “singer’s nodules” or “teacher’s nodules,” are benign growths that form on the vocal cords due to prolonged vocal strain or misuse. Common causes include:
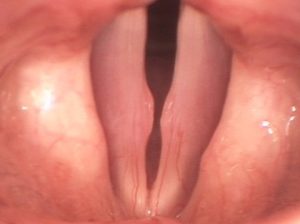
- Excessive vocal use: Frequent shouting, singing, or talking loudly.
- Poor vocal technique: Straining the voice or using improper breathing while speaking or singing.
- Irritants: Exposure to smoke, allergens, or acidic reflux can exacerbate vocal cord irritation.
- Occupation-related strain: Professions requiring extensive voice use, such as teaching, acting, or sales.
Symptoms
Vocal cord nodules can lead to noticeable changes in voice quality and other discomforts, such as:
- Hoarseness or a breathy voice.
- A reduced vocal range, especially for high notes in singers.
- Vocal fatigue or a sensation of strain while speaking or singing.
- Persistent throat clearing or a feeling of something in the throat.
- Pain or discomfort in the throat after prolonged voice use.
Treatment
Treatment for vocal cord nodules typically focuses on reducing vocal strain, healing the vocal cords, and improving vocal habits. Options include:
- Voice Rest: Temporarily limiting vocal use to allow the nodules to heal.
- Speech or Voice Therapy: Working with a speech-language pathologist to learn proper vocal techniques and reduce strain.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Hydrating adequately to keep vocal cords moist.
- Avoiding irritants such as smoking or exposure to dry air.
- Managing acid reflux if it contributes to irritation.
- Medications: If related to reflux or allergies, medications can reduce inflammation and irritation.
- Surgery: In rare and severe cases, when conservative measures fail, surgical removal of the nodules may be necessary.
Early intervention and consistent vocal care can often reverse the condition and prevent recurrence. If symptoms persist, consult an otolaryngologist (ENT specialist) for a thorough evaluation and tailored treatment plan.